The Strategic Management Process
The Internal Organization:
Resources, Capabilities, Core Competencies and Competitive Advantages
Overview: Eight content areas
- Importance of understanding internal organization
- Value: Definition and importance
- Tangible vs intangible resources
- Capabilities: Definition and development
- Core competencies: Criteria (N=4)
- Value Chain Analysis
- Outsourcing: Definition and “why?”
- Importance of internal organization assessment
CASE : Innovation vs. Efficiency: 3M
Diversified technology into 6 business segments.Historically: Commitment to innovation. Slogan: The Spirit of Innovation. That’s 3M.Relied on skills of scientists and engineers.Historically 1/3 annual sales from products introduced into marketplace in most recent 5 yrs. 30-plus core technologies basis for > 55,000 products
Changing times: by mid-2007 only 25% sales earned from products introduced over previous 5 yrs – why?
Leadership:1
CEO McNerney (formerly of GE) implemented Six-Sigma, a management technique to decrease product defects and increase efficiency.Six Sigma doesn’t lend itself to creativity / innovation, something imperative in the R&D arena.
Six Sigma
Focuses on actions to define, measure, analyze, improve and control – efficiency
Leadership:2
New CEO Buckley – a reenergization of R&D1.Importance of internal organization assessment
Analyzing the Internal Organization (IO)
- Context of Internal Analysis
- ‘Global mind-set’
- Ability to study an internal environment in ways that do not depend on the assumptions of a single country, culture, or context
- Analyze firm’s portfolio of resources and bundle heterogeneous resources and capabilities
- Understand how to leverage these bundles
- An organization's core competencies creates and sustains its competitive advantage
Creating Value
By Exploiting core competencies or competitive advantage, firms creates VALUE for customers
Value: measured by a product's performance characteristics and by its attributes for which customers are willing to pay
Firms wt Competitive advantage offers better value to customers then the value that competitor provides.
Value created by innovatively bundling and leveraging their resources and capabilities
Firms UNABLE to creatively do so..create value for customer but suffer performance decline.e.g.GM Visual DesignDurability, reliability,Milage & low cost.
The Challenge of Analyzing the IO
Strategic decisions that the Mgrs take about the components of their firms IO are non-routine, have ethical implications and influence the organization’s above-average returns
Involves identifying, developing, deploying and protecting firms’ resources, capabilities and core competencies
Evidences suggest that one-half of org decisions fail
Misidentifying Capabilities as core competencies but does not create Competitive advantage e.g. Polaroid Corporation.
Managers face uncertainty on many fronts --
Proprietary technologies
Changes in economic and political trends, societal values and shifts in customer demands
Environment – increases complexity .e.g. Gregory H.Boyce –CEO of PEABODY Engg.Corp.-World Largest COAL Co.- Dirty Fuel
Intra-organizational conflict
Due to decisions about core competencies and how to nurture them
Conditions Affecting Managerial Decisions About Resources, Capabilities, and Core Competencies
Resources, Capabilities and Core Competencies
- Resources
- Bundles to created organizational capabilities
- Tangible and intangible
- Capabilities
- Source of a firm’s core competencies and basis for CA
- Purposely integrated to achieve a specific task/set of tasks
- Core Competencies
- Capabilities that serve as a source of CA for a firm over its rivals
- Distinguish a company from its competitors – the personality
Tangible Resources:-
- Assets that can be seen, touched and quantified
- Value of Tangible Resources can be established thru financial Statements
- Value of Tangible Resources is constrained bcoz they are hard to liverage
- i.e.Same plane at 5 different routes at same time
Examples:
- equipment,
- facilities,
- distribution centers,
- formal reporting structures
Tangible resources fig
Intangible
- Assets rooted deeply in the firm’s history, accumulated over time
- In comparison to ‘tangible’ resources, usually can’t be seen or touched
- Examples:
- knowledge,
- trusts,
- organizational routines,
- capabilities,
- innovation,
- brand name,
- reputation
Intangible Resources chart:
Building Core Competencies: Criteria and Value Chain Analysis
Fig BCC
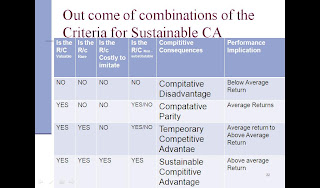
1.Four specific criteria of Sustainable CA
- Valuable
- Rare
- Costly-to-imitate
- Nonsubstitutable capabilities
Competitive consequences include
- Disadvantage, parity, temporary advantage and sustainable advantage
Performance implications include returns
- Above, below or average
Out come of combinations of the Criteria for Sustainable CA
chart:
2.Value Chain Analysis
- Primary activities
- Involved with product’s physical creation, sales and distribution to buyers, and service after the sale
- Service, marketing/sales, outbound/inbound logistics and operations
- Support activities
- Provide assistance necessary for the primary activities to take place
- Includes firm infrastructure, HRM, technologies development and procurement
Outsourcing
Definition: Purchase of a value-creating activity from an external supplier
- Effective execution includes an increase in flexibility, risk mitigation and capital investment reduction
- Trend continues at a rapid pace
- Firms must outsource activities where they cannot create value or are at a substantial disadvantage compared to competitors
- Usually revolves around innovative ability and loss of jobs
Competencies, Strengths, Weaknesses and Strategic Decisions
- Firms must identify their strengths and weaknesses
- Appropriate resources and capabilities needed to develop desired strategy and create value for customers/other stakeholders
- Tools (I.e., outsourcing) can help a firm focus on core competencies as the source for CA
- Core competencies have potential to become core rigidities
- Competencies emphasized when no longer competitively relevant can become a weakness
- External environmental conditions and events impact a firm’s core competencies
....Thanks






No comments:
Post a Comment